握力を増強、筋肉の疲労も低減
7月6日、GMは、ISS(国際宇宙ステーション)で使用する技術の開発に関してパートナーシップを結んでいるNASAと共同開発したロボットグローブ、「RoboGlove」を発表した。RoboGloveの技術はスウェーデンの医療技術会社のBioservo Technologies ABにライセンス供与され、医学的リハビリテーションや筋力を要する分野での補助装置として活用されていくとのことだ。
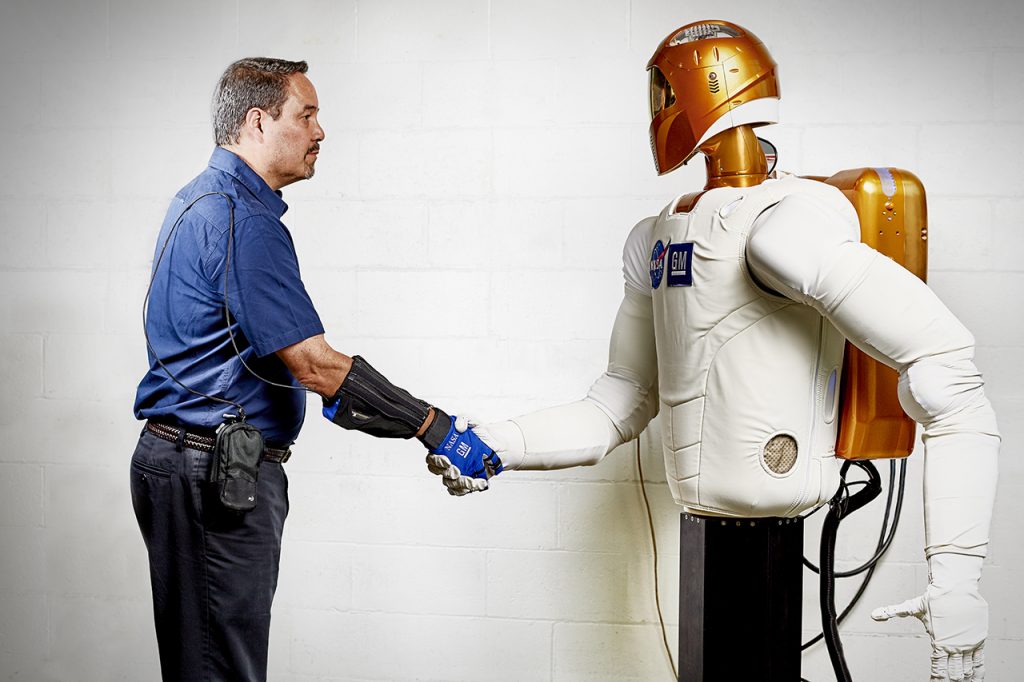

GMとNASAが共同開発をはじめたのは9年前からで、2011年には宇宙空間での活動を目的にした人型ロボットの「Robonaut 2」を発表。バッテリーを動力源に、装着する人間の動作に同期して筋力を補助するRoboGloveには、その時に開発された技術が投入されている。ライセンスを受けたBioservoは、今後、装着者の筋肉疲労を軽減しながらオペレーション効率を高める、さまざまな補助デバイスを開発していくという。
-

-
Text:Hidemitsu HOSHIGA Photo:GENERAL MOTORS COMPANY, LLC
-

-

-
Technology behind RoboGlove, an exo-muscular device that enhances strength and grip through leading-edge sensors, actuators and tendons that are comparable to the nerves, muscles and tendons in a human hand, is being licensed to Bioservo Technologies AB, a Swedish medical technologies company that will combine RoboGlove with its owner patented SEM glove technology, resulting in a glove that GM will purchase for testing in several of its plants next year.
-

-
The RoboGlove developed by GM and NASA is a “force multipler” that adds strength and grip to the human hand to allow more consistent effort when performing repetitive tasks. Research shows fatigue can occur within a few minutes of continuously gripping a tool. GM is licensing the RoboGlove intellectual property to Bioservo Technologies AB, a Swedish medical technologies company that will combine RoboGlove with its owner patented SEM glove technology.